The first step is to define material determination data in the message, and the second is to process it in the ERP system. SAP ERP, both ECC and S/4, provides several options for EDI integration, and EDI interchange using the IDOC-based approach is still widespread in the SAP world.
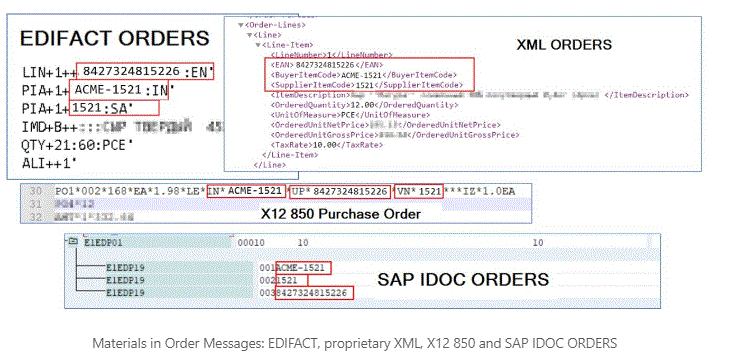
SAP standard IDOC processing offers very useful ready-made solutions. There is a segment, E1EDP19 Document Item Object Identification, dedicated to material determination and qualifiers for the identifiers in question:
- 001 Material number used by customer
- 002 Material number used by vendor
- 003 International Article Number(EAN)
As result all three examples above are mapped in the same IDOC data as follows:

If the SAP standard FM IDOC_INPUT_ORDERS is assigned for processing inbound orders, the sequence of determination steps will be as follows:
- SAP material number, Qualf = 002. If the value is wrong, IDOC fails regardless of other qualifiers
- CMIR, Qualf = 001. If the value is wrong, the system tries EAN or fails if EAN isn’t provided
- EAN, Qualf = 003. If the value is wrong, the IDOC fails
As a result a Sales order will be created based on the IDOC.

Several SAP-standard technique might work behind the scene. The most important are the following
Customer-Material Info records (t-codes VD51, VD52, VD53)
Both have some benefits and trade-offs and might be applied in combination. They are pretty powerful tools, and proper use of these features allows meeting most business requirements without extra development.